If you have to choose between OLED or LED screen then you must know how these technologies will work. If you’ve just got into business displays, or are shopping for the personal effects, knowledge of the main differences will help you during your purchase. You must know about the comparison because every technology has its strengths which impact picture quality, efficiency, and overall experience.
Table of Contents
What is an LED Screen?

An LED screen is a flat panel display that is used to produce images by using light-emitting diodes (LED’s). These LED’s are individual pixels, and when electricity flows into them it will give off the light. It makes LED screens able to spit out bright and clear visuals. You can use LED’s in such devices as televisions, computer monitors, and digital signage, they are commonly used.
What is an OLED Screen?

OLED screens function using organic compound substances which generate light output when electricity passes through them. Whereas a typical LED screen is made from a set of these individual pixels, each pixel on an OLED display generates its light, so no backlight is required. This helps produce deeper blacks, a higher contrast ratio, and more vibrant colors. The devices that have OLED screens are smartphones, televisions, and monitors.
Top 10 Key Differences Between OLED and LED Screens

Light Emission Mechanism
OLED: In OLED screens, each pixel emits its light. This self-emissive property makes it true black and has a high contrast ratio. When you see an OLED display, all the pixels turn on or off independently, producing ultra-black with vivid color. So an immersive view is produced.
LED: If you’ve seen LED screens, also known as LED-backlit LCDs, you have seen an example of these devices. This light is modulated by the liquid crystal layer to produce images. For that, you need true blacks which means the backlight is on always. Instead, blacks are replaced by dark grays. This influences the whole contrast and depth of the image.
Black Levels and Contrast
OLED: In OLED screens, each pixel emits its light. This is helpful in fully turning off pixels, thereby producing true black levels. Deep blacks and high contrast ratios are enjoyed due to a lack of backlight. A feature like this makes the viewing a lot more pleasing in dark places.
LED: The display of the LED screen is backed by a backlight. At true black levels, even local dimming is hard to do. OLED has no backlight, although they can cause light bleed so less deep blacks and lower contrast than a backlight. In the final stretch of your image which is dark in tone, this can influence the general picture quality.
Brightness
OLED: OLED screens have their light source and so can have deep blacks and high contrast. Nevertheless, they are generally less bright in peak brightness compared to LED screens. This makes them ideally suited to any kind of dark area, but less appropriate for illuminated ones. OLEDs have been improved in brightness in recent years and are more versatile now than previously.
LED: There is backlighting in LED screens, making possible higher peak brightness levels. They are therefore suitable for bright rooms and daylight viewing. The drawback is that the backlight can result in blooming effects, where light bleeds from bright areas into the dark. The problem can be avoided with high-end LED TVs with local dimming zones.
Viewing Angles
OLED: They have exceptional viewing angles. Color and contrast degradation can be viewed from nearly any angle and the display is easy to view from virtually any angle. This is because each pixel is lighting itself, resulting in consistent quality images throughout the screen. The picture is clear and the one is nice either if you are sitting directly in front or off to the side.
LED: LED screens especially ones with IPS panels are favorable from the viewing angle point of view. The image quality however can diminish when looking at it from sharp angles. They affect colors with a washed-out appearance and decreased contrast. The reason why this limitation exists is because LED screens require backlighting and backlighting has bad light leakage and can impact image consistency in oblique angles.
Response Time and Motion Blur
OLED: With OLED screens, you will get excellent real response times, which can be as little as 1 millisecond! This speed pixel transition allows you to have clean images even as you dart at rapid speeds during this scene. However, an OLED has a problem with motion persistence blur, also referred to as MPRT, where pixels are left on the screen for a long time. This can give the motion an unnatural feel which is not smooth.
LED: The response (or response) time of LED screens is usually 1 to 16 milliseconds slower than that of OLEDs. However, its consequence may be noticeable motion blur, especially from rapid motion. To counter this some LED displays use black frame insertion or motion interpolation. The methods for reducing motion blur might induce other visual artifacts.
Thickness and Flexibility
OLED: You will find OLED screens so thin and flexible. The reason is that the two pixels in one row will each emit their light, therefore without the need for a backlight. With this design, manufacturers can develop displays that are as slim as bendable. The production of innovative items including foldable smartphones together with curved televisions becomes possible through this flexible approach.
LED: On the other hand, LED screens tend to be tougher and more rigid. The pixels are reliant on a backlight to illuminate the pixels, making the device thicker. As such, this backlighting system limits the flexibility of the display which is not ideal for applications that his curved or foldable screens.
Power Consumption
OLED: The energy efficiency of OLED displays becomes maximized when viewers encounter dark material on-screen. It can also be shut off completely to turn off each pixel so it gives true blacks and significantly decreases power usage. However, it is known to consume more power, when displayed with bright or white content.
LED: Provider of LED screen for outdoor advertising, sunlight can bring down the brightness of the screen completely, but will not affect the backlight. It will be on due to the content on the screen. Since the image brightness has practically no impact on the power consumption, the constant backlight usage means power consumption is rather close to being constant.
Lifespan and Burn-in
OLED: OLED screens are known for their outstanding picture quality and vibrant colors. You will find them a desirable alternative but they have a shorter lifespan than LED screens. OLEDs use organic materials which tend to degrade with time, and brightness and color accuracy tends to drop. Permanently destruction screen conditions known as burn-in can occur in OLED screens when displaying uniform images.
LED: It have a longer lifetime than OLEDs. The duration before they stop working due to heat damage is shorter than other components but prolonged usage leads to better durability. This is advantageous in well-lit environments as LED’s can offer higher brightness levels. LED technology has improved, but, like most TVs, it still relies on a backlight, and for that reason, the uniformity of brightness and color within the screen is still an issue.
Cost and Availability
OLED: In most cases, OLEDs are more expensive than the LED model. It is associated with a complex manufacturing process and is comprised of organic materials, which means its cost is higher. OLED TVs and monitors therefore often tend to have a rather premium price tag. Despite this, prices have been gradually reduced with modern advancements.
LED: LED displays are usually less costly. The manufacturing process is well established and hence the production costs are lower. Affordability is such that LED TVs and monitors are popular choices among budget-conscious consumers. On top of that, LED displays are easily available in various sizes and different models such that you will find a wide range of options you can choose from.
Applications
OLED: OLED technology will find its way into smartphones, tablets, as well as high-end televisions. With its self-radiant pixel, it is thin and flexible and its color is bright and it’s black deep. OLED is very suitable for portable electronics and premium home entertainment systems. OLED also offers flexibility that allows new forms in wearable and automotive displays.
LED: LCD screens are widely used in different areas therefore, there is no need for further development. Backlighting for them is already possible with the help of LED technology—bright and energy-efficient ones, too! The speakers will include televisions, computer monitors, and smartphones with LED backlit displays. Due to their durability and cost-effectiveness LED’s are also used in signage, automotive lighting, and general illumination.
Pros and Cons of OLED vs LED Screen

It is important to remember the pros and cons of each screen. Whether you go for the cheaper LED, or the higher quality OLED depends entirely on your situation.
OLED Screens
Pros:
- Best Contrast: Each pixel in OLED screens shows light individually which creates the best possible contrast for black color reproduction.
- Wide Viewing Point: Screens produce consistent color appearance coupled with high contrast levels across different outlook which results in their superiority.
- Thin and Flexible Design: OLED displays are incredibly lightweight and flexible, allowing for innovation and stylish designs.
- Fast Response Time: The quick pixel response in these screens reduces motion blur during fast content such as gaming or sports.
Cons:
- Higher Cost: The manufacturing complexity associated with OLED screens causes them to cost more money because of their production requirements.
- Potential Burn-In: Static display of images over extended periods can lead to permanent ghost images that might form during this time.
- Lower Brightness: Similar to the above point, these screens are also unsuitable for overly bright rooms since they are incapable of reaching peak brightness levels.
- Shorter Lifetime: OLED screens have a less lifetime because the biotic material humiliate with the passage of time.
LED Screens
Pros:
- Energy Efficient: While OLED screens tend to use more power, LED screens are relatively more energy efficient due to lower power consumption.
- Use in Bright Areas: When compared to other display technologies, LED screens shine in well-lit areas because of their bright displays.
- Durability: LED screens usually last longer due to more advanced technology.
- Affordability: Since LED screens are cheaper to produce, they are sold at lower prices to consumers.
Cons:
- Poor Contrast: Unlike OLED displays, LED screens can never have deep blacks or high contrast ratios.
- Restricted Viewing Angles: The image quality becomes worse at wider angles, thus limiting flexibility.
- Heavier Design: LED displays are often thicker and heavier than OLEDs, making them more difficult to integrate into design.
- More Motion Blur: When compared to an OLED display, LED screens have worse quality when showing fast parts in movies and video games.
In the end, the choice depends on your priorities. Whether you need the brightness, efficiency, and affordability of LED or the superior contrast and design of OLEDs.
OLED vs LED Screen – Which One Is Better?
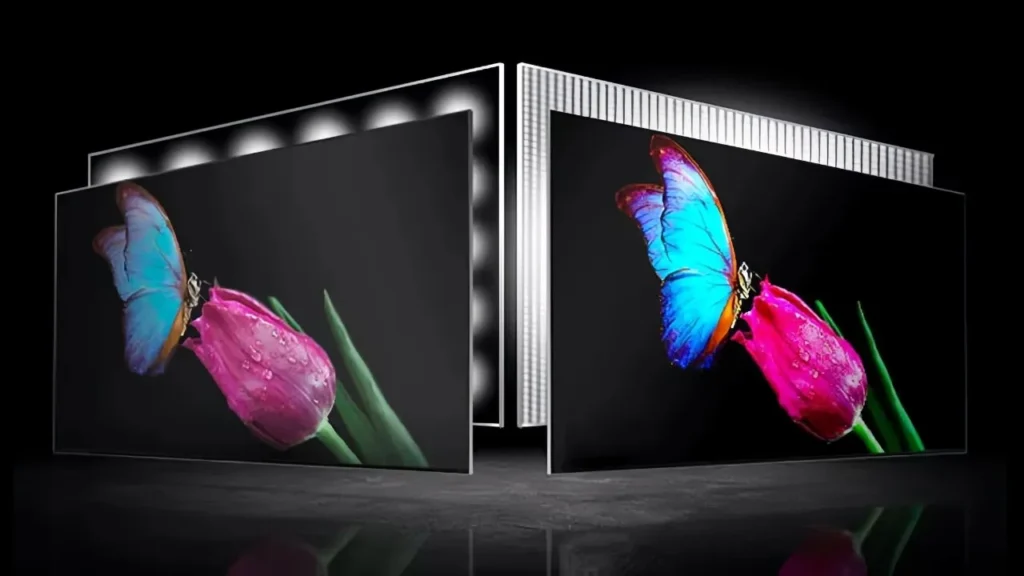

Consider your goals before picking between OLED or LED screens. OLED screens are more costly than their counterparts, but they typically have a longer lifespan. Color accuracy alongside contrast is often improved on OLED screens, which makes them perfect for high-quality visuals in darker settings.
On the other hand LED screens are affordable and capable of working in well-lit rooms while lasting as long as or longer than OLED screens. Adjustments between budget, viewing environment, and image quality will need to be made to come to a final decision.
Conclusion

To conclude, picking the appropriate screen technology requires you to understand the differences first. You need to manage your budget and assess your needs. OLED displays may offer better contrast while LED displays are becoming more accessible and economical. IvanLED is the right choice when it comes to OLED and LED screens.
FAQs

Can OLED screens be repaired if damaged, or do they require full replacement?
Repairing a broken OLED screen is a difficult process, as most of the time the panel will have to be completely replaced. Some people try to perform DIY repairs, but this is tricky due to the availability of replacement panels. Professional repair shops might offer the panel option, although this will depend on the manufacturer and model.
Can OLED screens be made flexible or foldable?
Yes, OLED technology is flexible both on the vertical and horizontal planes. Manufacturers have even produced flexible OLEDs that are capable of bending and folding without losing quality. These displays can be found in bendable smartphones and rollable televisions. For instance, LG created a rollable OLED TV, and Samsung presented its range of foldable OLED smartphones.